PM Methodology
Product Management Methodology (PMM)
______
The importance of delivering and maintaining the ‘right product’ at the ‘right time’ and in the ‘right place’ cannot be overstated and as such, each product
/service within a portfolio requires timely and appropriate action if the desired outcomes are to be achieved. ‘Best practice Product Management is a ‘critical
success factor’ for delivering world class products and services in alignment with planned expectations'.
The PMM is a robust (Agile / Lean) management process for strategically delivering market driven Products and Services. The methodology incorporates a
flexible planning framework that incorporates best practice business processes /procedures ensuring every aspect of the discipline are appropriately managed
against a market driven time frame.
The PMM is a definitive process developed by IPM from many years of practical experience in delivering best in class products / services and can be considered
as a best practice framework for the professional PM practitioner. Developed from first principles the PMM™ promulgates significant improvements within the
product management discipline which in turn provides the following positive benefits;
•
Traceable and audit-able Product Management procedures.
•
A complete understanding of ‘what needs to be achieved’.
•
Consistent and repeatable qualities directly associated with products.
•
Processes that can be accurately audited.
•
Identification and recognition of critical success factors and KPI’s.
•
Effective multi-disciplinary team management.
•
Embedded ‘market driven’ Innovation Management planning.
•
Improved requirements definition - Leading to Competitive advantage
•
Reduced time to market
' ...best practice robust method distilled from 30+ years of practical professional experience '
The PMM architecture is both robust and flexible but also ensures products are managed in a consistent and professional manner. Where applicable, processes
are supported by software models and associated tools which will in turn reiterate a consistent approach throughout the Product Management community.
‘To realise ‘best in class’ the Product Manager must be in complete control of their product portfolio(s) which in turn align
with the company’s overall strategy at all times’
The work flow approach of the PMM methodology has been specifically designed to increase the throughput of products and ensures total alignment with the
overall company strategy. This ultimately results in absolutely nothing being missed or overlooked. The process architecture also ensures that the fundamental
activity of managing products throughout their ‘life cycle’ is not diluted in any way and appropriately aligns required activities
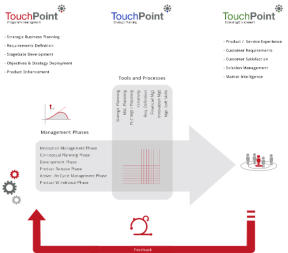
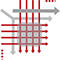
The above (diagram) PMM framework is one of four (generic) variant frameworks that successfully align the Product Management activity into a wide range of
businesses.
Operationally, the PMM framework promulgates an ethos of making it happen with Goals, Objectives and Strategies cascaded from the very top of the Company by the
use of highly focused multidisciplinary teams, led by Product Management. As such, the product teams are wholly responsible and fully accountable for driving the
Product / Service through every part of the organisation, from the cradle to the grave - in short, every functional area must know and understand what is expected from
them.
The above rationale will have the desired effect of making the 'Product Management' activity (...which includes the Product Manager, Market Development and Product
Director) the 'contracts giver/provider' to the operational environment - this simple alignment (or re-alignment for some companies) robustly makes everything crystal
clear, the outcomes of which, once implemented are nothing short of compelling. It is perhaps a bold generic statement to make, but from our 25+ years practical
experience, any other Product Management alignment is simply full of compromises with many disadvantages.
With the PMM alignment framework in place, each function within the Operational base plays their own part in a strategically aligned multi-disciplinary team
environment. Furthermore, managing individual products or portfolio of products across their life-cycles, the strategic business programme is always under-review, this
promulgates a constant desire for pro-active Continuous improvement.
PMM 'frameworks' have also been developed from first principles and feature an open architectural footprint - future proof. This means you able to robustly manage a
portfolio of Products / Services across individual 'life-cycles' in the knowledge that it is structurally sound and flexible enough to be rolled out across 'any' business unit.
Obviously there is no such thing as a 'generic business', they come in all shapes and sizes with their own unique quirks and idiosyncrasies. As such this must be to be
taken into account when deploying any management processes - it has to be right for the organisation concerned - a management process that is an incorrect fit or
goes against the culture will be badly received and soon fall into disrepute. Senior management must therefore believe in the system / process with a passion and
results will undoubtedly flow thereafter.
Strategic Product Management - Discipline Alignment Maps...
PMM Methodology - Product LifeCycles
Product Management activities lie at the heart of the (Product) LifeCycle process. As the name suggests a ‘LifeCycle’ is a time related series of events managed in
accordance with the requirements of an actioned strategy. Timing also plays a big part in this rationale. The ‘ethos’ of managing the Product LifeCycle is well understood
(…in theory) however in practice it becomes somewhat nebulous as there are many variables to be taken into account which are not entirely under our immediate
control.
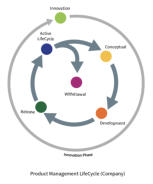
There are effectively two LifeCycles that must be managed. The first of which is the Product Management LifeCycle which is an internal management activity and
comprises of six phases:
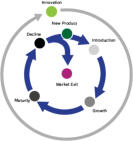
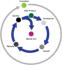
As you can see from the diagram below, the Innovation Phase completely surrounds the other 5 phases of Product Management and is by definition a perpetual activity
- it should definitely not be seen as a 2 week 'think and sprint' prior to a new product development project. Strategically, the role of Product Management is to manage
the Product across it's entire Product LifeCycle with the objective of maintaining its product position within the target market. Depending upon the market itself, this will
inevitably require enhancements and tweaks that ensures it remains competitive as long as possible against competing offers.
Joined up Thinking Personified
______
The PMM process architecture is the result of many years of research and study into the most efficient and effect way to create and manage products across their
entire life-cycle. The PMM process has been designed with utmost flexibility and can be deployed as a powerful stand alone methodology or seamlessly integrated into
other strategic planning processes, for example integration into the 'Business Canvas Model' enabling robust deployment of strategic objectives and critical success
factors.
Each of the time related phases of the PMM process have been meticulously cross mapped against an array of ‘best practice’ tools and processes (...with new tools
introduced as required). Without question the PMM process simply exudes unique qualities and to instill confidence further, you can be assured that throughout the
development activity we utilised resources gathered from highly respected academic studies and extensive professional experience.
The benefits to your organisation include:
•
Agile / Lean multi-disciplinary team management approach.
•
A professional understanding of ‘what needs to be achieved by whom and when’.
•
Traceable Product Management actions and procedures.
•
Seamless integration to other best practice methods.
•
Promotes consistent and repeatable qualities.
•
Robust delivery of strategic intent - Management by objectives.
•
Comprehensive Product Life-Cycle Management.
The defined work-flow approach provides significant viability and related benefits for the CEO, Directors and Product Group Managers alike. Product plans created by
the Product Manager provide continuous and consolidated reporting from the multidisciplinary team. As the product moves through the defined phases, absolute
control is maintained with every aspect concerning the strategy and expected performance reported as required.
‘Best practice Product Management is a ‘critical success factor’ for delivering world class
products and services in alignment with planned expectations’
The PMM™ architecture is both robust and flexible but also ensures products are managed in a consistent and professional manner. Where applicable, processes are
supported by software models and associated tools which will in turn reiterate a consistent approach throughout the Product Management community.
‘To realise ‘best in class’ the Product Manager must be in complete control of their product
portfolio(s) which in turn align with the company’s overall strategy at all times.
Best Practice in Action
______
…a key success factor is a competitive organisation. Products and Services are the lifeblood of the company and as such, must be given appropriate management
attention if desired outcomes are to be achieved. Each product / service within the overall portfolio will follow its own ‘life cycle’, a result of strategic intent and actioned
tactical plans. The level of commercial success achieved by each product/service within the portfolio, typically relates to how well market requirements have been
satisfied and directly to the ‘standard’ of ‘product management’ they have received.
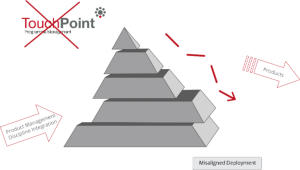
The consequences of misaligned strategic deployment
______
'A strategy without deployment and execution is only a plan... an intention'
From our own research, we found that many businesses (including some with well known brands) sadly operate in a totally inefficient and sometimes ineffective way
regarding the management of their own products and services. This typically leads to misaligned deployment and unavoidable inefficiencies. This obviously then has a
negative relationship with the level of achievement of market share, growth and profitability etc. ...But why should this be the case particularly from well known
respected companies? ...of course there are complex reasons for this situation. Not least of which that over many years there has been little formal development in the
field of Product Management and as such it is often the case that products and services are managed in a somewhat ad-hoc manner. The generic PMM process
provides a professional solution to the above... Analysis, Planning and Control...
Market Drivers for Products and Services
______
In a competitive environment market dynamics are constantly changing and evolving; Customers /Users are demanding products and services that align more precisely
with their individual needs and requirements. This promulgates greater expectations from the product offering and it’s not uncommon to find features that were once
‘unique and exciting’ rapidly becoming ‘basic or core’ attributes within a relatively short time span. The effect is amplified if product features can easily be copied or
substituted by competitor offerings. ‘Products and Services that have little or no product differentiation may be forced to compete on augmented attributes including
price which may not be appropriate or desired’ From a market perspective, a continuous cycle of product / service improvements and enhancements, progressively
raise the overall expectations of the customer base, which then become mandatory requirements going forward. Those involved in Product Management should be
aware of these idiosyncrasies and must pay particular attention to the requirements definition process, product positioning, value analysis and the ongoing product
portfolio strategy.
The Activity of Managing Products
______
A key role of the Product Manager is to ‘develop’ and 'manage' competitive advantage within defined commercial boundaries and targets. Innovation plays a major part
in satisfying the above and requires a thorough understanding of the needs and potential solutions of tomorrow’s markets. Innovation by definition is the result of
‘applied creativity’ and requires a constant flow of creative ideas to fuel this process. Quality ideas from creative workshops are screened for their strategic fit / level of
inventiveness before starting their development journey and eventually becoming the competitive advantage of tomorrow. Once achieved, maintaining competitive
advantage is prerequisite to product /service longevity and should be at the strategic core of the product management activity. This in turn reinforces the need for
continuous ‘innovation’ and ‘product development’ programmes. Best practice Product Management ensures that any proposed improvements and/or developments
are cross functionally supported and are in total alignment with the overall strategic plan.
Managing the evolution of technologies/customer needs is a critical success factor- Agility is therefore a fundamental element in Product Management.
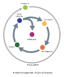
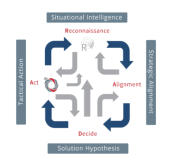
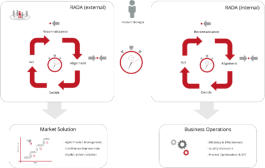
RADA(R) Loop and Product Management
______
In a highly competitive market environment of constant evolution, the need for a pro-active strategic approach is vital.
RADA(R) is a continuous sequence of…
Reconnaissance, Alignment (Strategic), Deciding and Acting. The integration culminated in the provision of two primary
RADA(R) loops. The first loop is biased toward the Marketing Environment where the Product Manager is on constant watch for user requirements and any strategic
objectives that are under threat. The second loop is dedicated to the internal Operational Environment and fulfills the task of optimising quality, efficiencies and costs.
The RADA(R) loop is fully supported / integrated with the proprietary TouchPoint methods.
Continuous Improvement Embedded Ethos
External (Market) Continuous Improvement
Internal Continuous Improvement
RADA(R) was created and developed by Steve Heron, IPM Copyright, 2008
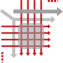
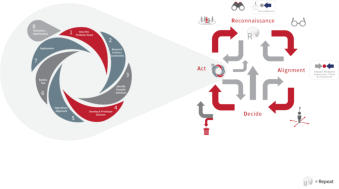
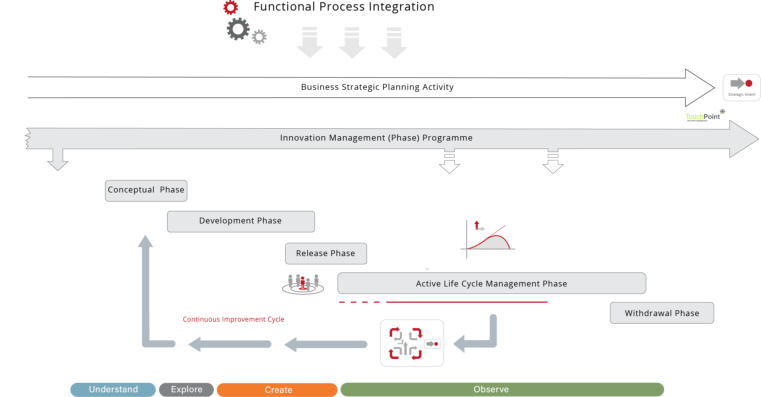
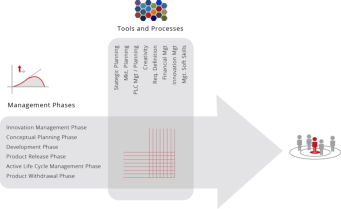
PMM Methodology – Design Architecture Fundamentals
______
Each phase of the PMM has been mapped against 40+ ‘best practice' tools and processes (some of which have been appropriately enhanced to fulfill specific
requirements) that guide and support the Product Manager through the life cycle of the product / portfolio...
When we developed the PMM™ process, ‘interdependencies matrices’ confirmed the relative importance of individual tools and processes throughout. It is therefore with
confidence we can say that the process supports best practice in all aspects of Product Management
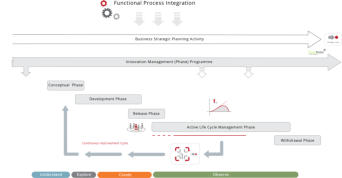
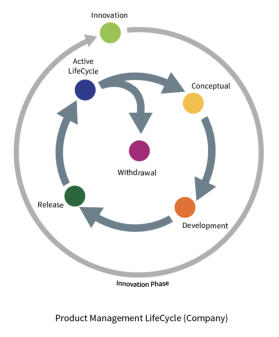
The Methodology comprehensively covers the entire end to end process from Ideation, Conceptual Planning, Product Development, Market Release, Active Life cycle
Management and finally into Product Withdrawal. Each of the stages mentioned above are mapped into specific time frames as follows;
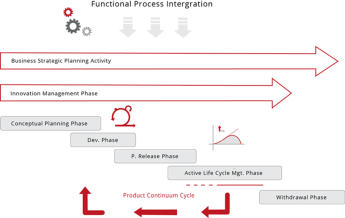
The above diagram indicates a route for ‘product revision’ and or ‘product replacement’, this section being brought into the process during the ‘Active Lifecycle
Management phase’ in the form of a ‘Product Continuum Cycle’. This in turn places appropriate emphasis on small incremental improvements (to maintain competitive
advantage) across the product lifecycle which would be in precise alignment with strategic intention and market position.
PM Processes and Tools ~ Element Interrelationship
______
Each of the process tools and process elements residing within the PMM process are all supported with business models and templates. Within each element itself is a
comprehensive overview of the subject area and how any supporting business model should be used.
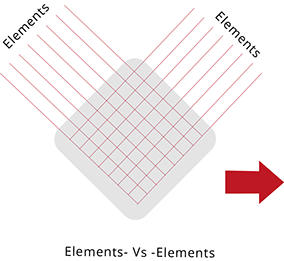

PM Processes and Tools ~ Element Interrelationship
______
Interactive Business Models are complemented with over 30 individual interactive business models. Each ‘element’ within the process is partnered with a specific
business model, designed to help provide PM’s and Directors communicate and manage with confidence, resulting in quality strategic decisions being made.
Interactive business models have been designed to be easy to use and understand yet produce a strong visual impact when presented. Needless to say the Product
Manager feels eminently comfortable using them as part of their own planning activities. The business models themselves provide for suitable prescriptive comments
against the concluding visual position which is then taken on board for further strategic analysis. The models are populated with your specific data and if challenged can
be appropriately defended or interactively changed to meet with an agreed position (in other words the model is further calibrated with all parties buying into the final
position).
The PMM Process is complemented by best practice processes and procedures software/ business models include some of the following;
•
Market Segmentation
•
Boston Matrix
•
Ansoff Matrix
•
MFP Matrix
•
Product Positioning
•
SWOT Analysis
•
Objectives + Strategies
•
Critical Success Factors
•
Kano Model
•
QFD (Quality Function Deployment)
•
PEST Analysis
•
Feature & Benefit Analysis
•
Product Viability Modeling
•
Financial Modeling
•
Pricing
Note: If required, Business models can be customised to meet the specific requirements of your company / business. Business models can be purchased
separately, please contact us for further information.
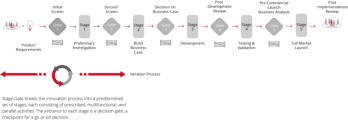
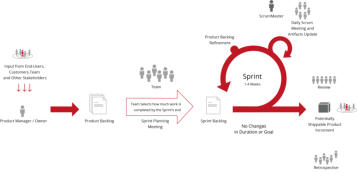
PMM and NPD (New Product Development) Processes
______
The PMM methodology fully embraces whatever development process you have adopted (Waterfall, agile (Scrum), Kanban and Hybrid) at your company. A
selection of the most common development processes include the following;


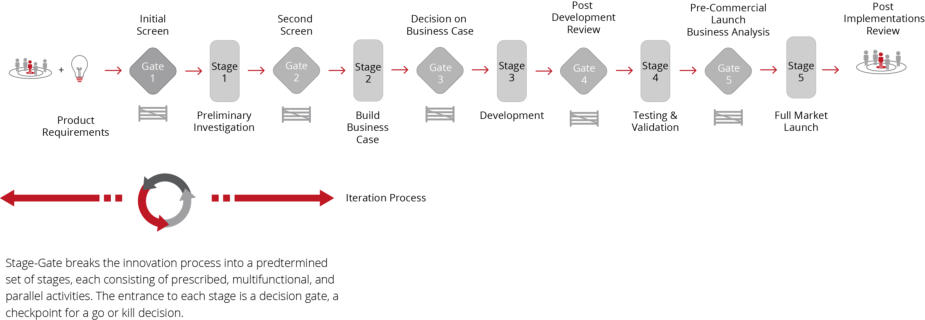
Stage Gate
Agile (Scrum)
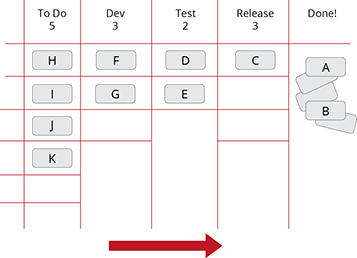
Kanban
| Professional Training & Support

Location

Tel: +44 (0)1202 699870

|Contact
Email: info.request@ipm-marketing.co.uk
Follow us:
©1996-2023 Innovation Process Management



Innovation Process Management
Unit 4 - 6
147b Wareham Road
Corfe Mullen
Wimborne, Dorset
BH21 3LA
United Kingdom

PM Methodology
Product Management Methodology (PMM)
______
The importance of delivering and maintaining the ‘right
product’ at the ‘right time’ and in the ‘right place’ cannot be
overstated and as such, each product /service within a
portfolio requires timely and appropriate action if the desired
outcomes are to be achieved. ‘Best practice Product
Management is a ‘critical success factor’ for delivering world
class products and services in alignment with planned
expectations'.
The PMM is a robust (Agile / Lean) management process for
strategically delivering market driven Products and Services.
The methodology incorporates a flexible planning framework
that incorporates best practice business processes
/procedures ensuring every aspect of the discipline are
appropriately managed against a market driven time frame.
The PMM is a definitive process developed by IPM from many
years of practical experience in delivering best in class
products / services and can be considered as a best practice
framework for the professional PM practitioner. Developed
from first principles the PMM™ promulgates significant
improvements within the product management discipline
which in turn provides the following positive benefits;
•
Traceable and audit-able Product Management
procedures.
•
A complete understanding of ‘what needs to be achieved’.
•
Consistent and repeatable qualities directly associated
with products.
•
Processes that can be accurately audited.
•
Identification and recognition of critical success factors
and KPI’s.
•
Effective multi-disciplinary team management.
•
Embedded ‘market driven’ Innovation Management
planning.
•
Improved requirements definition - Leading to
Competitive advantage
•
Reduced time to market
' ...best practice robust method distilled from 30+ years of
practical professional experience '
The PMM architecture is both robust and flexible but also
ensures products are managed in a consistent and
professional manner. Where applicable, processes are
supported by software models and associated tools which will
in turn reiterate a consistent approach throughout the
Product Management community.
‘To realise ‘best in class’ the Product Manager must be in
complete control of their product portfolio(s) which in turn
align with the company’s overall strategy at all times’
The work flow approach of the PMM methodology has been
specifically designed to increase the throughput of products
and ensures total alignment with the overall company
strategy. This ultimately results in absolutely nothing being
missed or overlooked. The process architecture also ensures
that the fundamental activity of managing products
throughout their ‘life cycle’ is not diluted in any way and
appropriately aligns required activities
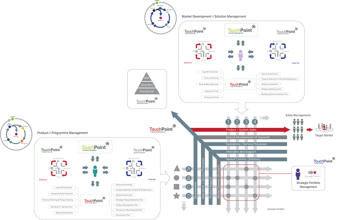
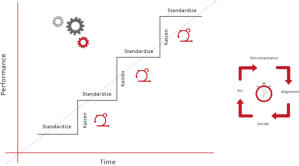
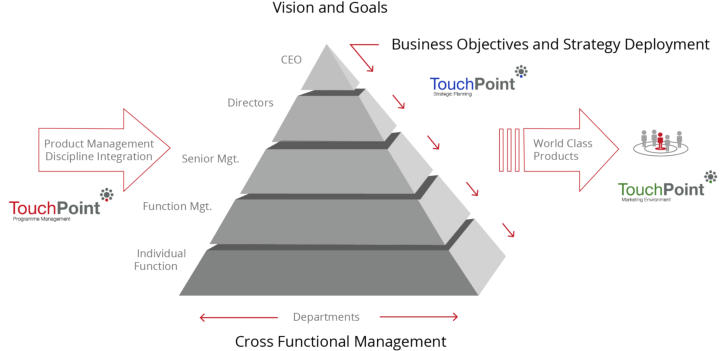
The above (diagram) PMM framework is one of four (generic)
variant frameworks that successfully align the Product
Management activity into a wide range of businesses.
Operationally, the PMM framework promulgates an ethos of
making it happen with Goals, Objectives and Strategies
cascaded from the very top of the Company by the use of
highly focused multidisciplinary teams, led by Product
Management. As such, the product teams are wholly
responsible and fully accountable for driving the Product /
Service through every part of the organisation, from the
cradle to the grave - in short, every functional area must know
and understand what is expected from them.
The above rationale will have the desired effect of making the
'Product Management' activity (...which includes the Product
Manager, Market Development and Product Director) the
'contracts giver/provider' to the operational environment -
this simple alignment (or re-alignment for some companies)
robustly makes everything crystal clear, the outcomes of
which, once implemented are nothing short of compelling. It
is perhaps a bold generic statement to make, but from our
25+ years practical experience, any other Product
Management alignment is simply full of compromises with
many disadvantages.
With the PMM alignment framework in place, each function
within the Operational base plays their own part in a
strategically aligned multi-disciplinary team environment.
Furthermore, managing individual products or portfolio of
products across their life-cycles, the strategic business
programme is always under-review, this promulgates a
constant desire for pro-active Continuous improvement.
PMM 'frameworks' have also been developed from first
principles and feature an open architectural footprint - future
proof. This means you able to robustly manage a portfolio of
Products / Services across individual 'life-cycles' in the
knowledge that it is structurally sound and flexible enough to
be rolled out across 'any' business unit. Obviously there is no
such thing as a 'generic business', they come in all shapes
and sizes with their own unique quirks and idiosyncrasies. As
such this must be to be taken into account when deploying
any management processes - it has to be right for the
organisation concerned - a management process that is an
incorrect fit or goes against the culture will be badly received
and soon fall into disrepute. Senior management must
therefore believe in the system / process with a passion and
results will undoubtedly flow thereafter.
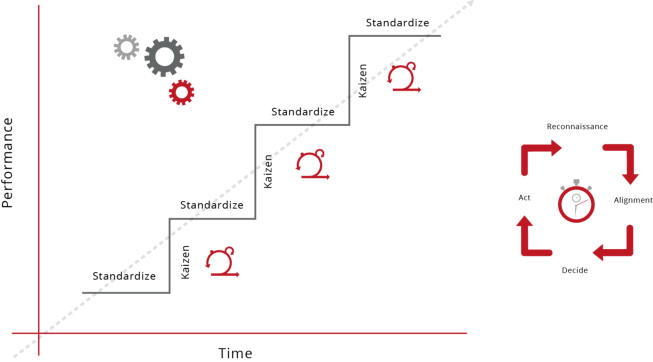
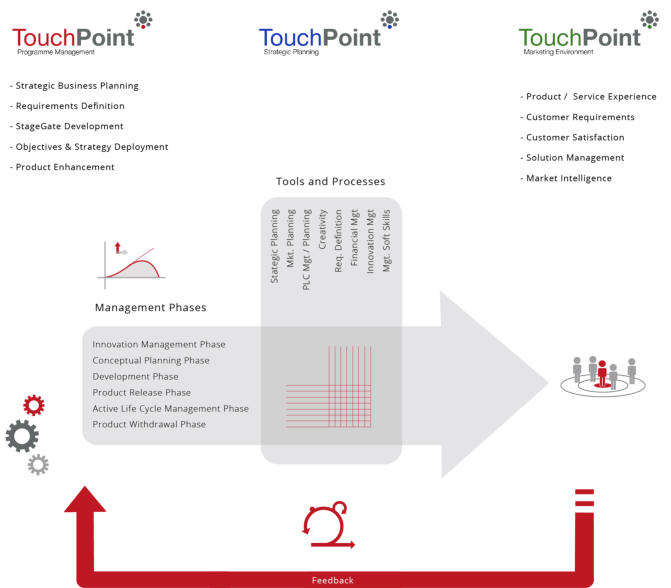
Strategic Product Management - Discipline Alignment Maps...

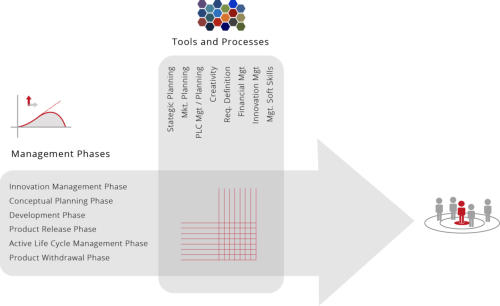
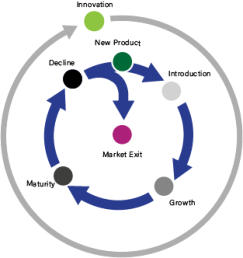
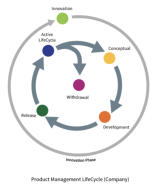
PMM Methodology - Product LifeCycles
Product Management activities lie at the heart of the
(Product) LifeCycle process. As the name suggests a ‘LifeCycle’
is a time related series of events managed in accordance with
the requirements of an actioned strategy. Timing also plays a
big part in this rationale. The ‘ethos’ of managing the Product
LifeCycle is well understood (…in theory) however in practice it
becomes somewhat nebulous as there are many variables to
be taken into account which are not entirely under our
immediate control.
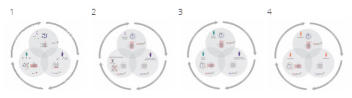
There are effectively two LifeCycles that must be managed.
The first of which is the Product Management LifeCycle which
is an internal management activity and comprises of six
phases:
As you can see from the diagram below, the Innovation Phase
completely surrounds the other 5 phases of Product
Management and is by definition a perpetual activity - it
should definitely not be seen as a 2 week 'think and sprint'
prior to a new product development project. Strategically, the
role of Product Management is to manage the Product across
it's entire Product LifeCycle with the objective of maintaining
its product position within the target market. Depending
upon the market itself, this will inevitably require
enhancements and tweaks that ensures it remains
competitive as long as possible against competing offers.
Joined up Thinking Personified
______
The PMM process architecture is the result of many years
of research and study into the most efficient and effect
way to create and manage products across their entire
life-cycle. The PMM process has been designed with
utmost flexibility and can be deployed as a powerful stand
alone methodology or seamlessly integrated into other
strategic planning processes, for example integration into
the 'Business Canvas Model' enabling robust deployment
of strategic objectives and critical success factors.
Each of the time related phases of the PMM process have
been meticulously cross mapped against an array of ‘best
practice’ tools and processes (...with new tools introduced
as required). Without question the PMM process simply
exudes unique qualities and to instill confidence further,
you can be assured that throughout the development
activity we utilised resources gathered from highly
respected academic studies and extensive professional
experience.
The benefits to your organisation include:
•
Agile / Lean multi-disciplinary team management
approach.
•
A professional understanding of ‘what needs to be
achieved by whom and when’.
•
Traceable Product Management actions and
procedures.
•
Seamless integration to other best practice methods.
•
Promotes consistent and repeatable qualities.
•
Robust delivery of strategic intent - Management by
objectives.
•
Comprehensive Product Life-Cycle Management.
The defined work-flow approach provides significant
viability and related benefits for the CEO, Directors and
Product Group Managers alike. Product plans created by
the Product Manager provide continuous and
consolidated reporting from the multidisciplinary team. As
the product moves through the defined phases, absolute
control is maintained with every aspect concerning the
strategy and expected performance reported as required.
Best practice Product Management is a ‘critical success factor’
for delivering world class products and services in alignment
with planned expectations’
The PMM™ architecture is both robust and flexible but
also ensures products are managed in a consistent and
professional manner. Where applicable, processes are
supported by software models and associated tools which
will in turn reiterate a consistent approach throughout the
Product Management community.
‘To realise ‘best in class’ the Product Manager must be in
complete control of their product portfolio(s) which in turn
align with the company’s overall strategy at all times.
Best Practice in Action
______
…a key success factor is a competitive organisation.
Products and Services are the lifeblood of the company
and as such, must be given appropriate management
attention if desired outcomes are to be achieved. Each
product / service within the overall portfolio will follow its
own ‘life cycle’, a result of strategic intent and actioned
tactical plans. The level of commercial success achieved by
each product/service within the portfolio, typically relates
to how well market requirements have been satisfied and
directly to the ‘standard’ of ‘product management’ they
have received.
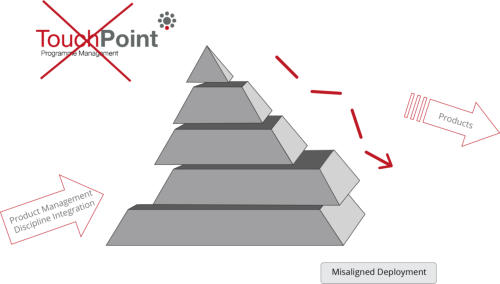
The consequences of misaligned strategic
deployment
______
'A strategy without deployment and execution is only
a plan... an intention'
From our own research, we found that many
businesses (including some with well known brands)
sadly operate in a totally inefficient and sometimes
ineffective way regarding the management of their
own products and services. This typically leads to
misaligned deployment and unavoidable
inefficiencies. This obviously then has a negative
relationship with the level of achievement of market
share, growth and profitability etc. ...But why should
this be the case particularly from well known
respected companies? ...of course there are complex
reasons for this situation. Not least of which that over
many years there has been little formal development
in the field of Product Management and as such it is
often the case that products and services are
managed in a somewhat ad-hoc manner. The generic
PMM process provides a professional solution to the
above... Analysis, Planning and Control...
Market Drivers for Products and Services
______
In a competitive environment market dynamics are
constantly changing and evolving; Customers /Users are
demanding products and services that align more
precisely with their individual needs and requirements.
This promulgates greater expectations from the product
offering and it’s not uncommon to find features that were
once ‘unique and exciting’ rapidly becoming ‘basic or core’
attributes within a relatively short time span. The effect is
amplified if product features can easily be copied or
substituted by competitor offerings. ‘Products and
Services that have little or no product differentiation may
be forced to compete on augmented attributes including
price which may not be appropriate or desired’ From a
market perspective, a continuous cycle of product /
service improvements and enhancements, progressively
raise the overall expectations of the customer base, which
then become mandatory requirements going forward.
Those involved in Product Management should be aware
of these idiosyncrasies and must pay particular attention
to the requirements definition process, product
positioning, value analysis and the ongoing product
portfolio strategy.
The Activity of Managing Products
______
A key role of the Product Manager is to ‘develop’ and
'manage' competitive advantage within defined
commercial boundaries and targets. Innovation plays a
major part in satisfying the above and requires a thorough
understanding of the needs and potential solutions of
tomorrow’s markets. Innovation by definition is the result
of ‘applied creativity’ and requires a constant flow of
creative ideas to fuel this process. Quality ideas from
creative workshops are screened for their strategic fit /
level of inventiveness before starting their development
journey and eventually becoming the competitive
advantage of tomorrow. Once achieved, maintaining
competitive advantage is prerequisite to product /service
longevity and should be at the strategic core of the
product management activity. This in turn reinforces the
need for continuous ‘innovation’ and ‘product
development’ programmes. Best practice Product
Management ensures that any proposed improvements
and/or developments are cross functionally supported
and are in total alignment with the overall strategic plan.
Managing the evolution of technologies/customer needs
is a critical success factor- Agility is therefore a
fundamental element in Product Management.
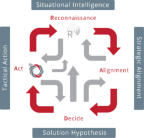
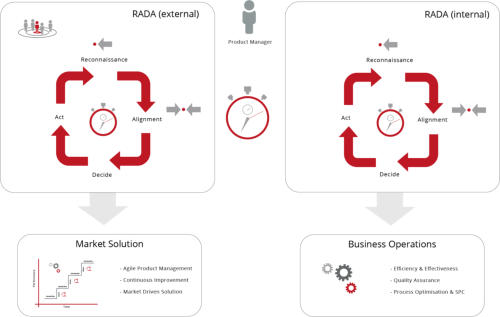
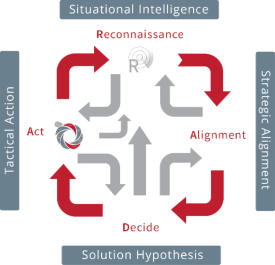
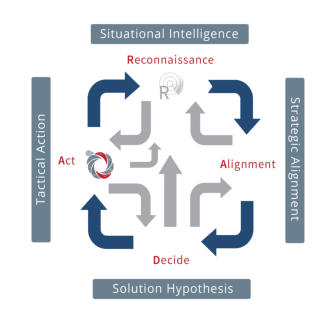
RADA(R) Loop and Product Management
______
In a highly competitive market environment of constant
evolution, the need for a pro-active strategic approach is
vital.
RADA(R) is a continuous sequence of…
Reconnaissance, Alignment (Strategic), Deciding and
Acting. The integration culminated in the provision of two
primary
RADA(R) loops. The first loop is biased toward the
Marketing Environment where the Product Manager is on
constant watch for user requirements and any strategic
objectives that are under threat. The second loop is
dedicated to the internal Operational Environment and
fulfills the task of optimising quality, efficiencies and costs.
The RADA(R) loop is fully supported / integrated with the
proprietary TouchPoint methods.
RADA(R) was created and developed by Steve Heron, IPM Copyright, 2008
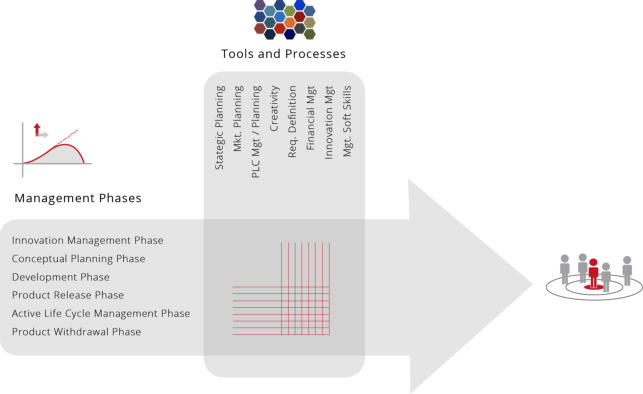
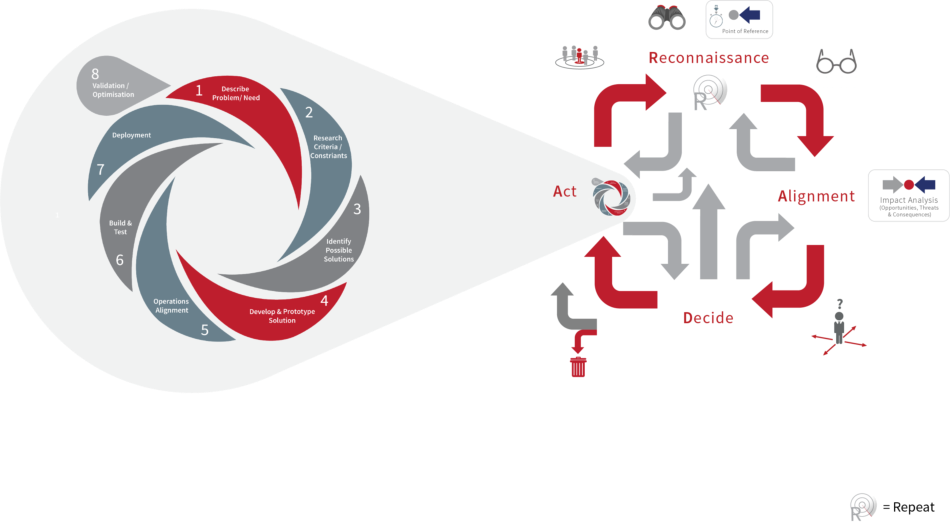
PMM Methodology – Design Architecture Fundamentals
______
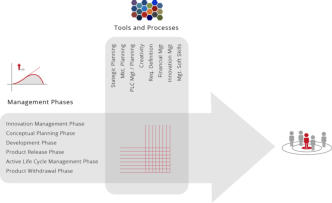
Each phase of the PMM has been mapped against 40+ ‘best
practice' tools and processes (some of which have been
appropriately enhanced to fulfill specific requirements) that
guide and support the Product Manager through the life
cycle of the product / portfolio...
When we developed the PMM™ process,
‘interdependencies matrices’ confirmed the relative
importance of individual tools and processes throughout. It
is therefore with confidence we can say that the process
supports best practice in all aspects of Product
Management
The Methodology comprehensively covers the entire end to
end process from Ideation, Conceptual Planning, Product
Development, Market Release, Active Life cycle
Management and finally into Product Withdrawal. Each of
the stages mentioned above are mapped into specific time
frames as follows;
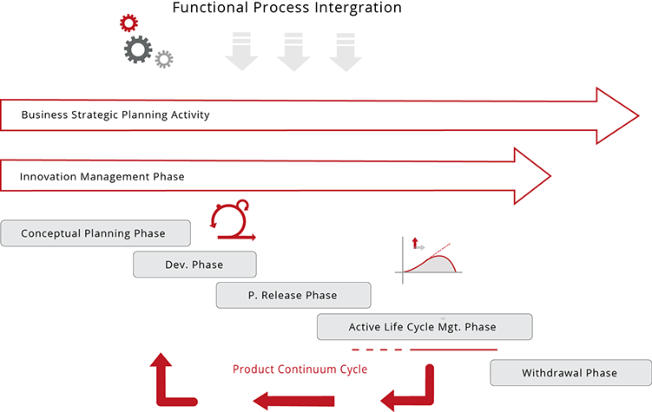
The above diagram indicates a route for ‘product revision’ and
or ‘product replacement’, this section being brought into the
process during the ‘Active Lifecycle Management phase’ in the
form of a ‘Product Continuum Cycle’. This in turn places
appropriate emphasis on small incremental improvements (to
maintain competitive advantage) across the product lifecycle
which would be in precise alignment with strategic intention
and market position.
PM Processes and Tools ~ Element Interrelationship
______
Each of the process tools and process elements residing
within the PMM process are all supported with business
models and templates. Within each element itself is a
comprehensive overview of the subject area and how any
supporting business model should be used.

PM Processes and Tools ~ Element Interrelationship
______
Interactive Business Models are complemented with over
30 individual interactive business models. Each ‘element’
within the process is partnered with a specific business
model, designed to help provide PM’s and Directors
communicate and manage with confidence, resulting in
quality strategic decisions being made.
Interactive business models have been designed to be easy to
use and understand yet produce a strong visual impact when
presented. Needless to say the Product Manager feels
eminently comfortable using them as part of their own
planning activities. The business models themselves provide for
suitable prescriptive comments against the concluding visual
position which is then taken on board for further strategic
analysis. The models are populated with your specific data and
if challenged can be appropriately defended or interactively
changed to meet with an agreed position (in other words the
model is further calibrated with all parties buying into the final
position).
The PMM Process is complemented by best practice processes
and procedures software/ business models include some of
the following;
•
Market Segmentation
•
Boston Matrix
•
Ansoff Matrix
•
MFP Matrix
•
Product Positioning
•
SWOT Analysis
•
Objectives + Strategies
•
Critical Success Factors
•
Kano Model
•
QFD (Quality Function Deployment)
•
PEST Analysis
•
Feature & Benefit Analysis
•
Product Viability Modeling
•
Financial Modeling
•
Pricing
Note: If required, Business models can be customised to meet
the specific requirements of your company / business.
Business models can be purchased separately, please contact
us for further information.
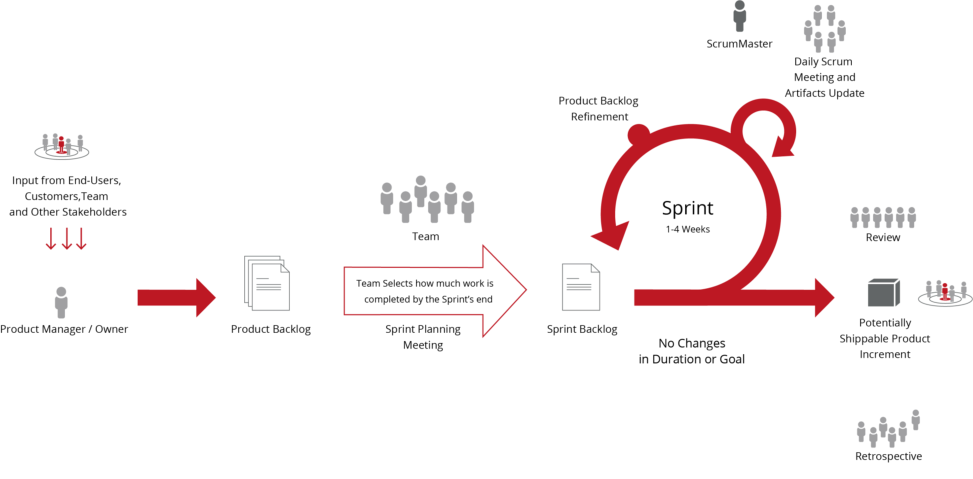
PMM and NPD (New Product Development) Processes
______
The PMM methodology fully embraces whatever development
process you have adopted (Waterfall, agile (Scrum), Kanban and
Hybrid) at your company. A selection of the most common
development processes include the following;




Stage Gate
Agile (Scrum)
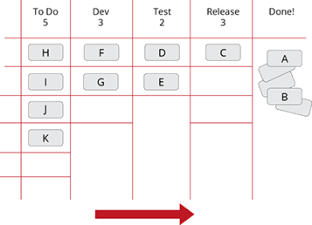
Kanban
Innovation Process Management
Unit 4 - 6
147b Wareham Road
Corfe Mullen
Wimborne, Dorset
BH21 3LA
United Kingdom

Location

Tel: +44 (0)1202 699870

|Contact
Email: info.request@ipm-marketing.co.uk
Follow us:

©1996-2019 Innovation Process Management
| Professional Training & Support